
A new data-thieving malware named BlackGuard is profitable the interest of the cybercrime neighborhood, now bought on many darknet marketplaces and message boards for a life time price of $700 or a subscription of $200 for each month.
The stealer can snatch delicate info from a wide selection of apps, pack every little thing in a ZIP archive and mail it to the C2 of the malware-as-a-company (MaaS) procedure.
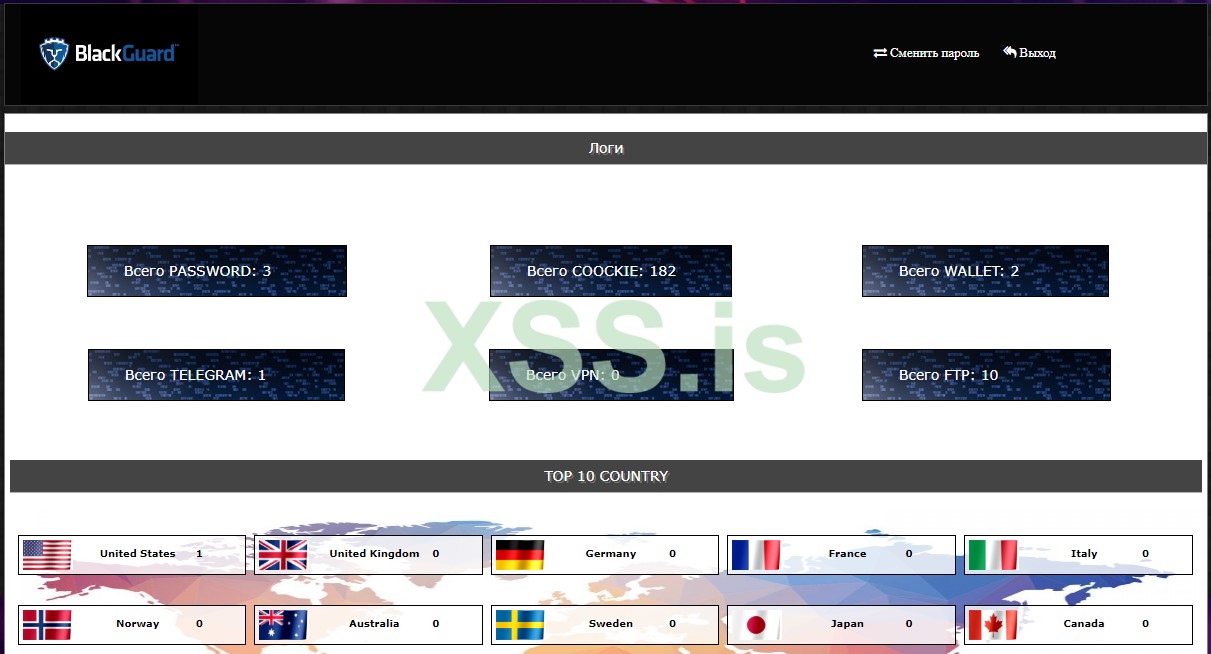
Risk actors who acquired the subscription can then obtain the BlackGuard internet panel to retrieve the stolen details logs, either exploiting them themselves or providing them to others.
BlackGuard was spotted and analyzed by scientists at Zscaler, who have observed a unexpected spike in the reputation of the malware, primarily after the abrupt shutdown of Raccoon Stealer.
Bleeping Computer system was in a position to come across that BlackGuard to start with appeared on Russian-speaking community forums in January 2022, circulated privately for tests applications.
.jpg)
Comprehensive stealing capabilities
As with all present day info-stealers, there aren’t quite a few apps storing or dealing with sensitive user information that are not in BlackGuard’s concentrating on scope, and the concentration is major on cryptocurrency belongings.
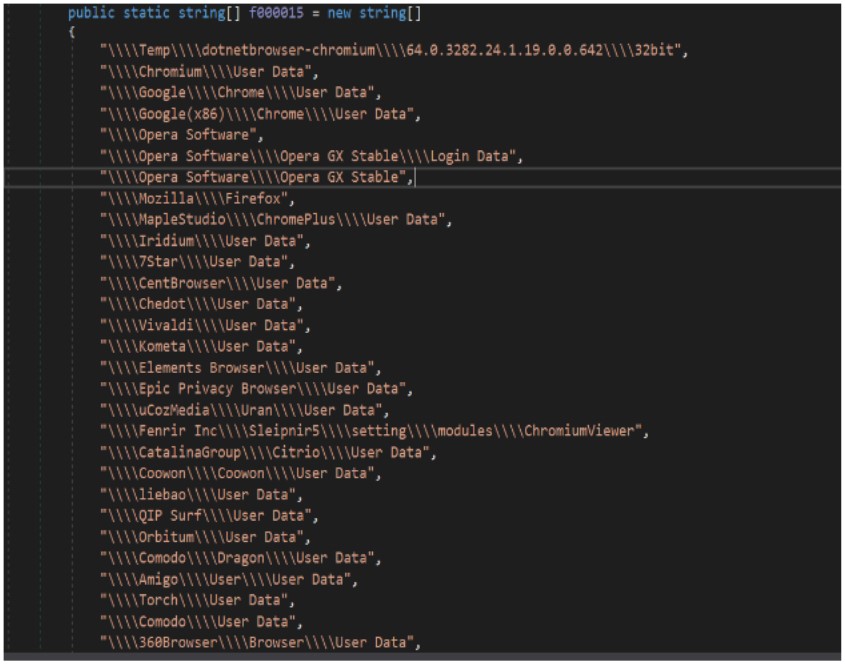
BlackGuard will find the presence of the following application and endeavor to steal person information from them:
- Web browsers: Passwords, cookies, autofill, and background from Chrome, Opera, Firefox, MapleStudio, Iridium, 7Star, CentBrowser, Chedot, Vivaldi, Kometa, Elements Browser, Epic Privacy Browser, uCozMedia, Coowon, liebao, QIP Surf, Orbitum, Comodo, Amigo, Torch, Comodo, 360Browser, Maxthon3, K-Melon, Sputnik, Nichrome, CocCoc, Uran, Chromodo, Edge, BraveSoftware
- Wallet browser extensions: Binance, coin98, Phantom, Mobox, XinPay, Math10, Metamask, BitApp, Guildwallet, iconx, Sollet, Slope Wallet, Starcoin, Swash, Finnie, KEPLR, Crocobit, OXYGEN, Nifty, Liquality, Auvitas wallet, Math wallet, MTV wallet, Rabet wallet, Ronin wallet, Yoroi wallet, ZilPay wallet, Exodus, Terra Station, Jaxx
- Cryptocurrency wallets: AtomicWallet, BitcoinCore, DashCore, Electrum, Ethereum, Exodus, LitecoinCore, Monero, Jaxx, Zcash, Photo voltaic, Zap, AtomicDEX, Binance, Frame, TokenPocket, Wassabi
- Email: Outlook
- Messengers: Telegram, Signal, Tox, Ingredient, Pidgin, Discord
- Other: NordVPN, OpenVPN, ProtonVpn, Totalcommander, Filezilla, WinSCP, Steam
The collected information and facts is bundled in a ZIP file, also recognised as logs, and despatched to the C2 server via a Submit request, alongside with a program profiling report that sets a exceptional hardware ID for the sufferer and determines their location.
Anti-detection features
BlackGuard’s evasion abilities are even now below large growth, but some methods are now in put to assist the malware escape detection and analysis.
Initial, it is packed with a crypter, and all its strings are base64 obfuscated, so several anti-virus resources relying on static detection will skip it.
Any AVs functioning on the technique will be detected by the malware, which will then endeavor to get rid of their processes and terminate their operation.
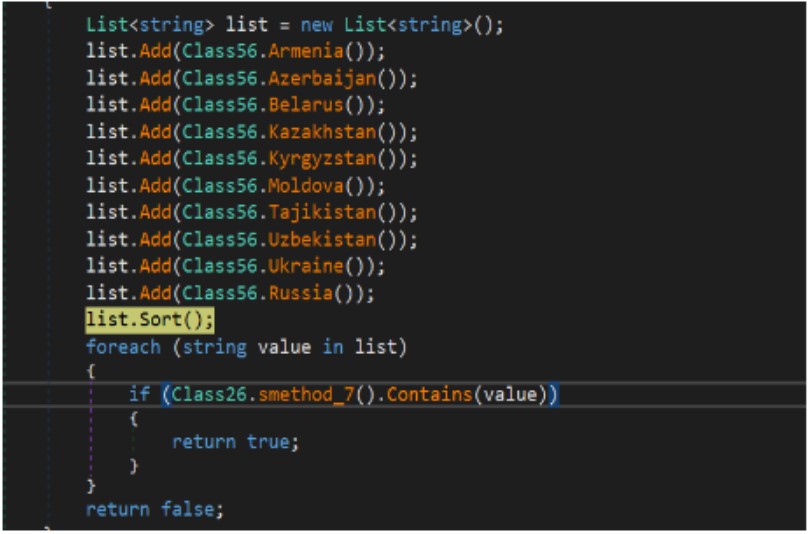
The malware also checks the victim’s IP handle, and if it’s jogging on a method in Russia or any other CIS country, it will prevent and exit. This is but a different indicator of the origin of the malware.
Last but not least, an anti-debug characteristic blocks the operation of the mouse and keyboard inputs, earning it additional tricky for researchers to analyze the malware.
Outlook
Details-stealers are on the rise, with Redline, MarsStealer, Vidar Stealer, and AZORult currently dominating the room.
The exit of Raccoon Stealer, which was just one of the most significant players, has left a hole in the cybercrime industry, so other MaaS operators will test to just take advantage of this development.
Daria Romana Pop, a threat analyst at KELA, has shared the adhering to insights with Bleeping Computer on the standing of the info-stealers landscape:
“Specified the maximize in usage and exploitation of compromised accounts and details obtained by info stealers as a vector for preliminary accessibility to a target, KELA has recently noticed new variants getting marketed on cybercrime forums, as menace actors aim at increasing the malware abilities to better stay clear of detection and to advance the knowledge collection and exfiltration processes.”
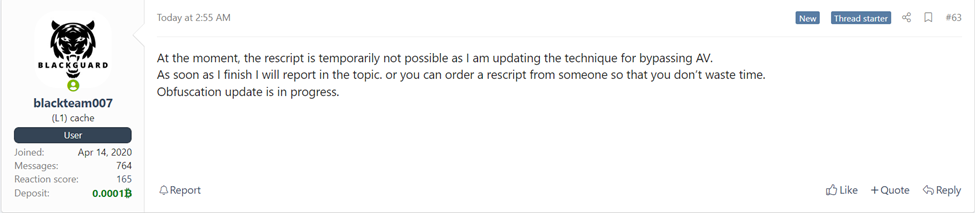
“BlackGuard stealer released in early 2021. As cybercriminals are continuously screening the capabilities of these malicious resources, they do not shy away from demanding more high-quality and advancements. KELA came across various latest conversations in which users were being complaining about BlackGuard not staying in a position to correctly stay clear of detection. As in any business enterprise, the operators promised to provide an up-to-date version in no time.”
“In a various state of affairs, KELA recognized META – a new details stealer extremely very similar in physical appearance to RedLine, whose collected data is remaining offered on the TwoEasy botnet market. The stealer was released at the beginning of March, now sold for USD125 for every thirty day period or USD1000 for endless use, and the operators assert that it is an enhanced model of RedLine.”
To defend by yourself from all of the circulating info-thieving malware, stay away from browsing shady sites and downloading files from untrustworthy or doubtful resources.
Last but not least, use two-aspect authentication, preserve your OS and applications up to day, and use powerful and special passwords for all your on the internet accounts.






